Introduction
Here, we will see how to create select, insert, update, and delete statements using stored procedures in SQL Server. Let's take a look at a practical example. We create a table.
Creating Database
Creating Table
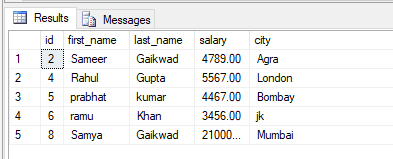
Now add some rows to the table. We can add new rows using an INSERT INTO SQL statement. Then execute a SELECT SQL query to display all records of the table.
The table looks like this.
Figure 1
Stored Procedure for Select, Insert, Update, Delete
Here, we create a stored procedure with SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE SQL statements. The SELECT SQL statement is used to fetch rows from a database table. The INSERT statement is used to add new rows to a table. The UPDATE statement is used to edit and update the values of an existing record. The DELETE statement is used to delete records from a database table. The following SQL stored procedure is used insert, update, delete, and select rows from a table, depending on the statement type parameter.
Now press F5 to execute the stored procedure. This will create a new stored procedure in the database.
Now open object explorer and select storeprocedure MasterInsertUpdateDelete.
Stored Procedure to Check Insert
StatementType = 'Insert'
MasterInsertUpdateDelete -> right click select Execute Stored Procedure...
Figure 2
Execute procedure window will be opened.
Figure 3
Now for insert, we fill the data in values in the required fields.
StatementType=insert
Figure 4
Click on the OK button.
You will see a new row added to the database table.
Figure 5
Stored Procedure to Check update
MasterInsertUpdateDelete -> right-click select Execute Stored Procedure...
Execute procedure window will be opened.
StatementType = 'Update'
Figure 6
Click on the OK button.
Check employee table with following updated data where id is 7.
Figure 7
Stored Procedure to Check Delete
MasterInsertUpdateDelete -> right-click select Execute Stored Procedure...
Execute procedure window will be opened.
StatementType = 'Delete'
Figure 8
We will delete records from the table which has id=2.
Click on the OK button. And check in the employee table with the following deleted data where id is 2.
Figure 9
Summary
A single stored procedure can be used to select, add, update, and delete data from a database table. In this article, we learned how to create a single stored procedure to perform all operations using a single SP in SQL Server.


















0 Comments