This article was originally published on mesameergaikwad as Joins In SQL Server #mesameergaikwad.
Joins In SQL Server
In this article, I am going to explain joins and types of joins with examples. Here we will be using SQL Server 2017 or you can use SQL Server 2008 or above.
Definition
Joins are used to fetch/retrieve data from two or more related tables from a database. In general, tables are related to each other using foreign key constraints.
Types of Joins
There are four types of joins in SQL Server.
- Inner Join
- Outer Join
- Cross Join
- Self Join
Again, Outer Joins are divided into three types.
- Left Join or Left Outer Join
- Right Join or Right Outer Join
- Full Join or Full Outer Join
Now, I am going to explain different types of joins with examples and the differences between them.
Prerequisites
SQL Server 2017 or you can use SQL server 2008 or above version.
Now, first, we will create a Database and two tables to apply the joins for understanding.
Creating Database and Two Tables
Step 1 — Create a Database
Open your SQL Server and use the following script to create the “sameer” Database.
- Create database sameer
Now, select the script query then press F5 or click on Execute button to execute the above script.
You should see a message, “Command(s) completed successfully.” This means your new database has been created.
Step 2 — Create the first table
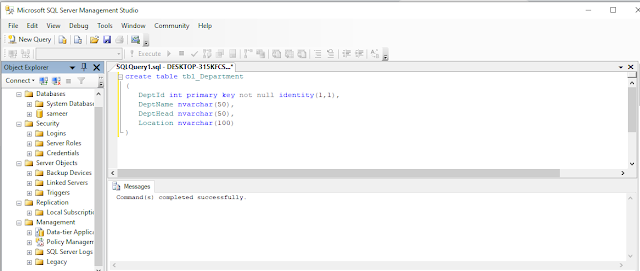
Open your SQL Server and use the following script to create table “tbl_Department”.
- create table tbl_Department
- (
- DeptId int primary key not null identity(1,1),
- DeptName nvarchar(50),
- DeptHead nvarchar(50),
- Location nvarchar(100)
- )
Execute the above query to create “tbl_Department “.
You should see a message, “Command(s) completed successfully.”
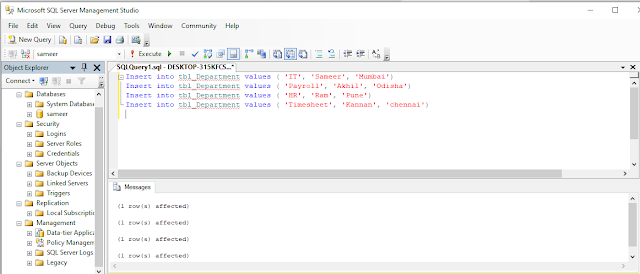
Now, data is inserted into the table.
- Insert into tbl_Department values ( ‘IT’, ‘Sameer’, ‘Mumbai’)
- Insert into tbl_Department values ( ‘Payroll’, ‘Akhil’, ‘Odisha’)
- Insert into tbl_Department values ( ‘HR’, ‘Ram’, ‘Pune’)
- Insert into tbl_Department values ( ‘Timesheet’, ‘Kannan’, ‘chennai’)
Execute the above query, you should see a message, “Command(s) completed successfully.”
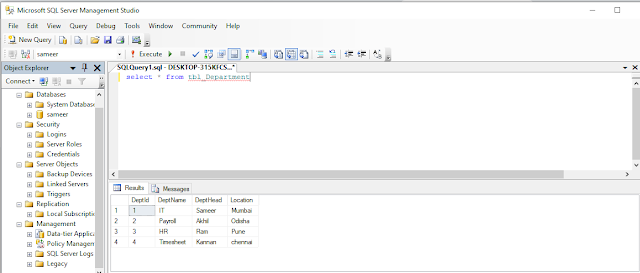
Now retrieve all data from the “tbl_Department” table.
- select * from tbl_Department
output
Step 3 — Create a second table
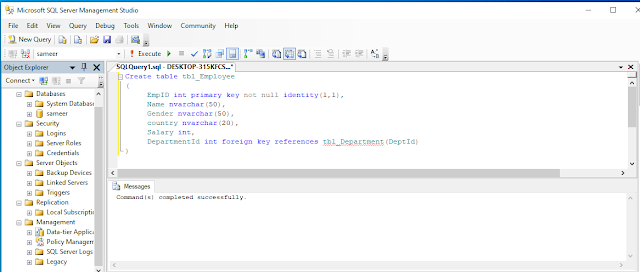
Open your SQL Server and use the following script to create table “tbl_Employee”.
- Create table tbl_Employee
- (
- EmpID int primary key not null identity(1,1),
- Name nvarchar(50),
- Gender nvarchar(50),
- country nvarchar(20),
- Salary int,
- DepartmentId int foreign key references tbl_Department(DeptId)
- )
Execute the above query to create “tbl_Employee “.
You should see a message, “Command(s) completed successfully.”
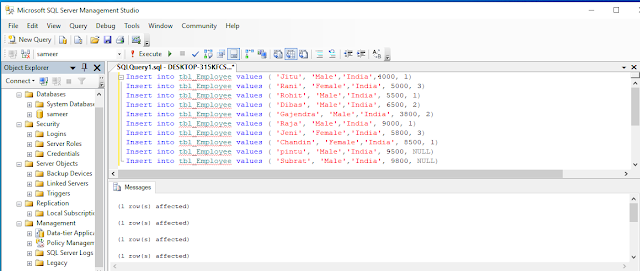
Now, data is inserted into the table.
- Insert into tbl_Employee values ( ‘Jitu’, ‘Male’,’India’,4000, 1)
- Insert into tbl_Employee values ( ‘Rani’, ‘Female’,’India’, 5000, 3)
- Insert into tbl_Employee values ( ‘Rohit’, ‘Male’,’India’, 5500, 1)
- Insert into tbl_Employee values ( ‘Dibas’, ‘Male’,’India’, 6500, 2)
- Insert into tbl_Employee values ( ‘Gajendra’, ‘Male’,’India’, 3800, 2)
- Insert into tbl_Employee values ( ‘Raja’, ‘Male’,’India’, 9000, 1)
- Insert into tbl_Employee values ( ‘Jeni’, ‘Female’,’India’, 5800, 3)
- Insert into tbl_Employee values ( ‘Chandin’, ‘Female’,’India’, 8500, 1)
- Insert into tbl_Employee values ( ‘pintu’, ‘Male’,’India’, 9500, NULL)
- Insert into tbl_Employee values ( ‘Subrat’, ‘Male’,’India’, 9800, NULL)
Execute the above query, you should see a message, “Command(s) completed successfully.”
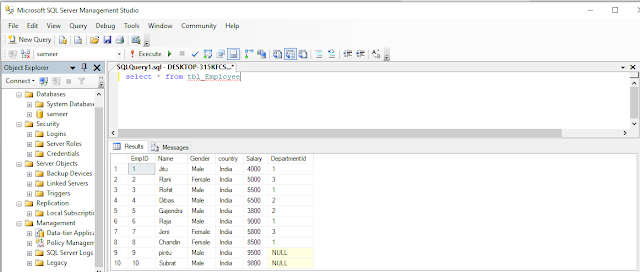
Now retrieve all data from the “tbl_Employee” table.
- select * from tbl_Employee
output
General Formula for Joins,
- SELECT ColumnList (whatever column you want to display)
- FROM LeftTableName
- JOIN_TYPE RightTableName
- ON JoinCondition
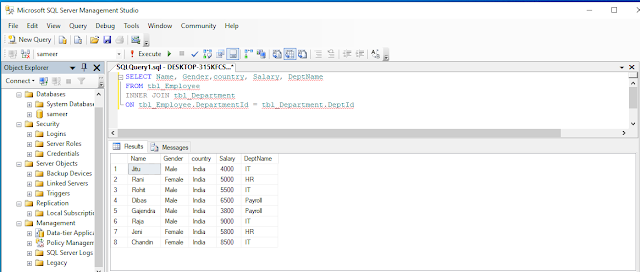
INNER JOIN
Inner join returns only the matching rows between both the tables; non-matching rows are eliminated.
Example
Write a query to retrieve Name, Gender, Country, Salary, and DeptName from tbl_Employee and tbl_Department table.
INNER JOIN Query
- SELECT Name, Gender,country, Salary, DeptName
- FROM tbl_Employee
- INNER JOIN tbl_Department
- ON tbl_Employee.DepartmentId = tbl_Department.DeptId
OR
- SELECT Name, Gender,country, Salary, DeptName
- FROM tbl_Employee
- JOIN tbl_Department
- ON tbl_Employee.DepartmentId = tbl_Department.DeptId
Note
JOIN or INNER JOIN is the same. It’s always better to use INNER JOIN.
OR
- select emp.Name,emp.Gender,emp.country,emp.Salary,dept.DeptName
- from tbl_Employee emp
- inner join tbl_Department dept
- on emp.DepartmentId=dept.DeptId
OutPut
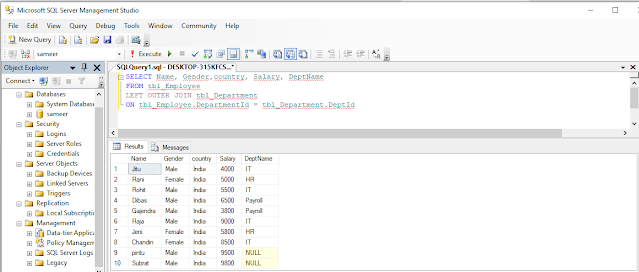
LEFT JOIN or LEFT OUTER JOIN
Left Join or Left Outer Join returns only the matching rows between both the tables, plus non-matching rows from the left table.
Example
Write a query to retrieve Name, Gender, Country, Salary, and DeptName from tbl_Employee and tbl_Department table.
LEFT JOIN or LEFT OUTER JOINQuery,
- SELECT Name, Gender,country, Salary, DeptName
- FROM tbl_Employee
- LEFT OUTER JOIN tbl_Department
- ON tbl_Employee.DepartmentId = tbl_Department.DeptId
OR
- SELECT Name, Gender,country, Salary, DeptName
- FROM tbl_Employee
- LEFT JOIN tbl_Department
- ON tbl_Employee.DepartmentId = tbl_Department.DeptId
Note
You can use, LEFT JOIN or LEFT OUTER JOIN. OUTER keyword is optional.
OR
- select emp.Name,emp.Gender,emp.country,emp.Salary,dept.DeptName
- from tbl_Employee emp
- LEFT JOIN tbl_Department dept
- on emp.DepartmentId=dept.DeptId
OutPut
RIGHT JOIN or RIGHT OUTER JOIN
Right Join or Right Outer Join returns only the matching rows between both the tables, plus non-matching rows from the right table.
Example
Write a query to retrieve Name, Gender, Country, Salary, and DeptName from tbl_Employee and tbl_Department table.
RIGHT JOIN or RIGHT OUTER JOIN Query,
- SELECT Name, Gender,country, Salary, DeptName
- FROM tbl_Employee
- RIGHT JOIN tbl_Department
- ON tbl_Employee.DepartmentId = tbl_Department.DeptId
OR
- SELECT Name, Gender,country, Salary, DeptName
- FROM tbl_Employee
- RIGHT OUTER JOIN tbl_Department
- ON tbl_Employee.DepartmentId = tbl_Department.DeptId
Note
You can use, RIGHT JOIN or RIGHT OUTER JOIN. OUTER keyword is optional.
OR
- select emp.Name,emp.Gender,emp.country,emp.Salary,dept.DeptName
- from tbl_Employee emp
- RIGHT JOIN tbl_Department dept
- on emp.DepartmentId=dept.DeptId
OutPut
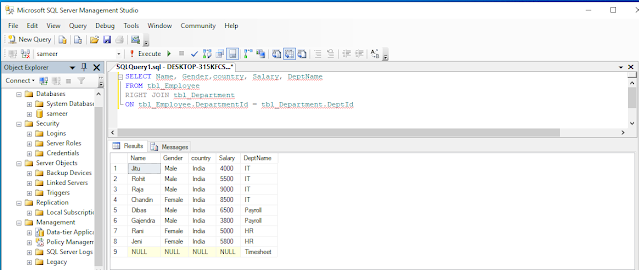
FULL JOIN or FULL OUTER JOIN
Full Join or Full Outer Join returns all rows from both the tables (left & right tables), including non-matching rows from both the tables.
Example
Write a query to retrieve Name, Gender, Country, Salary, and DeptName from tbl_Employee and tbl_Department table.
FULL JOIN or FULL OUTER JOIN Query,
- SELECT Name, Gender, country, Salary, DeptName
- FROM tbl_Employee
- FULL OUTER JOIN tbl_Department
- ON tbl_Employee.DepartmentId = tbl_Department.DeptId
OR
- SELECT Name, Gender, country, Salary, DeptName
- FROM tbl_Employee
- FULL JOIN tbl_Department
- ON tbl_Employee.DepartmentId = tbl_Department.DeptId
Note
You can use, FULL JOIN or FULL OUTER JOIN. The OUTER keyword is optional.
OR
- select emp.Name,emp.Gender,emp.country,emp.Salary,dept.DeptName
- from tbl_Employee emp
- FULL JOIN tbl_Department dept
- on emp.DepartmentId=dept.DeptId
OutPut
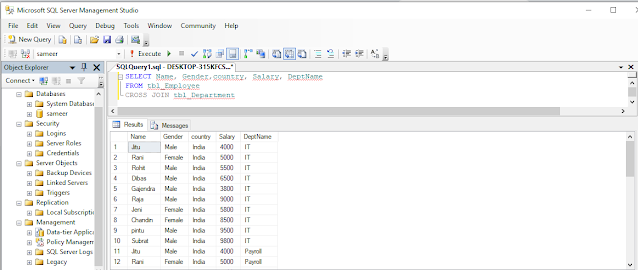
CROSS JOIN
CROSS JOIN, produces the Cartesian product of the 2 tables.
For example, in the tbl_Employee table, we have 10 rows and in the tbl_Department table, we have 4 rows. So, a cross join between these 2 tables produces 40 rows. Cross Join shouldn’t have an ON clause.
Example
Write a query, to retrieve Name, Gender, Country, Salary, and DeptName from tbl_Employee and tbl_Department table.
CROSS JOIN Query
- SELECT Name, Gender,country, Salary, DeptName
- FROM tbl_Employee
- CROSS JOIN tbl_Department
OR
- select emp.Name,emp.Gender,emp.country,emp.Salary,dept.DeptName
- from tbl_Employee emp
- cross JOIN tbl_Department dept
OutPut
Conclusion
In this article, I explained joins in SQL Server with examples. I hope this article has helped you to understand this topic. Post your valuable feedback in the comments section.





0 Comments